MXF to WMVConvert MXF to WMV, MXF to WMV Converter |
 |
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact |
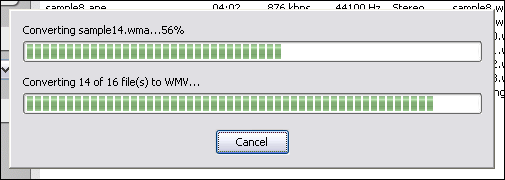
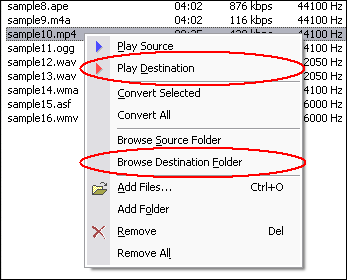
MXF to WMV Converter converts MXF to WMV. The software is an ALL-IN-ONE audio converter that supports more than 100 audio and video files. MXF to WMV Converter supports batch conversion and, is full compatible with Vista and Windows 7.
What is MXF? MXF has been designed by the leading players in the broadcast industry - with an enormous amount of input from the user community - to ensure that the format really meets their demands. It is being put forward as an Open Standard which means it is a file transfer format that is openly available to all interested parties. It is not compression-scheme-specific and it simplifies the integration of systems using MPEG and DV as well as future, as yet unspecified, compression strategies. This means that the transportation of these different files will be independent of content, and will not dictate the use of specific manufacturers¡¯ equipment. Any required processing can simply be achieved by automatically invoking the appropriate hardware or software codec. However, MXF is designed for operational use and so all the handling processes are seamless to the user. It just works quietly in the background. Besides offering better interoperability - working with video and audio between different equipment and different applications - its other major contribution is the transport of metadata. By developing MXF from the beginning as a new file format, considerable thought has gone into the implementation and use of metadata. Not only is this important for the proper functioning of MXF files, it will also enable powerful new tools for media management as well as improving the content-creation workflows by eliminating repetitive metadata re-entry. The changing technologies in television production, and in transmission to the viewers, means that the traditional methods for moving the content - programme video and audio - within studios is changing too. Not only is there far greater use of computers and IT-related products such as servers, but also the reliance on automation and the re-use of material have expanded. Besides the need to carry metadata, file transfers are needed to fit in with computer operations and they must be capable of being streamed for real-time operations. The development of the Material eXchange Format (MXF) is a remarkable achievement of collaboration between manufacturers and major organizations such as Pro-MPEG, the EBU and the AAF Association. It establishes interoperability of content between various applications used in the television production chain. This leads to operational efficiency and creative freedom through a unified networked environment. MXF is a "container" or "wrapper" format which supports a number of different streams of coded "essence", encoded with any of a variety of codecs, together with a metadata wrapper which describes the material contained within the MXF file. MXF was developed to carry a subset of the Advanced Authoring Format (AAF) data model, under a policy known as the Zero Divergence Directive (ZDD). This enables MXF/AAF workflows between non-linear editing (NLE) systems using AAF and cameras, servers, and other devices using MXF. What is WMV? A WMV file is in most circumstances encapsulated in the Advanced Systems Format (ASF) container format. The file extension .WMV typically describes ASF files that use Windows Media Video codecs. The audio codec used in conjunction with Windows Media Video is typically some version of Windows Media Audio, or in rarer cases, the deprecated Sipro ACELP.net audio codec. Microsoft recommends that ASF files containing non-Windows Media codecs use the generic .ASF file extension. The ASF container can optionally support digital rights management using a combination of elliptic curve cryptography key exchange, DES block cipher, a custom block cipher, RC4 stream cipher and the SHA-1 hashing function. Although WMV is generally packed into the ASF container format, it can also be put into the AVI or Matroska container format. The resulting files have the .AVI and .MKV file extensions, respectively. WMV can be stored in an AVI file when using the WMV 9 Video Compression Manager (VCM) codec implementation. Another common way to store WMV in an AVI file is to use the VirtualDub encoder. Windows Media Video (WMV) is the most recognized video format within the WMV family. Usage of the term WMV often refers to the Microsoft Windows Media Video codec only. Its main competitors are MPEG-4 AVC, AVS, RealVideo, DivX, and Xvid. The first version of the codec, WMV 7, was introduced in 1999, and was built upon Microsoft's implementation of MPEG-4 Part 2. Continued proprietary development led to newer versions of the codec, but the bit stream syntax was not frozen until WMV 9. While all versions of WMV support variable bit rate, average bit rate, and constant bit rate, WMV 9 introduced several important features including native support for interlaced video, non-square pixels, and frame interpolation. WMV 9 also introduced a new profile titled Windows Media Video 9 Professional, which is activated automatically whenever the video resolution exceeds 300,000 pixels (e.g., 528x576, 640x480 or 768x432 and beyond) and the bitrate 1000 kbit/s. It is targeted towards high-definition video content, at resolutions such as 720p and 1080p. Convert MXF to WMV Related Topics: MMF to WMV, DTS to WMV, MPP to WMV, ALAC to WMV, MIDI to WMV, ALAW to WMV, RA to WMV, WMA to WMV, RAM to WMV, ADX to WMV, M4R to WMV, M2A to WMV, AMR to WMV, MKA to WMV, W64 to WMV, WAVE64 to WMV, MTM to WMV, VQF to WMV, OGA to WMV, AC3 to WMV, RMJ to WMV, NSA to WMV, MPC to WMV, AU to WMV, UMX to WMV, ADTS to WMV, CAF to WMV, MOD to WMV, TTA to WMV
|
| Home | Getting Started | Download | Buy Now! | Screen Shots | FAQ | Support | Contact | Links |
| Copyright © 2007-2014 Hoo Technologies All rights reserved. Privacy Policy |